Notes:
Character chatbots and virtual beings represent two approaches to AI-driven interaction, with character chatbots focusing on text-based conversations within specific contexts or narratives through natural language processing, primarily used in customer service, entertainment, and education. In contrast, virtual beings, or digital humans, offer a more immersive experience by incorporating visual, auditory, and sometimes tactile elements to mimic human interactions closely, employing advanced AI, computer graphics, and animation. Virtual beings are utilized in a broader range of applications, including immersive customer service, healthcare, and as companions, highlighting the key differences in interaction modes, technological complexity, and application scope between the two.
Websites like Character.AI feature AI-driven characters that simulate human-like conversations using advanced natural language processing technologies. Users can interact with a diverse array of characters, from fictional creations to representations of historical figures, each with their own designed personalities. These platforms offer interactive and often customizable experiences, focusing on entertainment, education, or companionship.
PygmalionAI is an open-source conversational AI frontend that uses KoboldAI models fine-tuned on chat data from closed platforms like CharacterAI. It provides an actively developed 6B model optimized for chatting, along with guides for users to contribute their own data and improve the system. PygmalionAI’s goal is to replicate and eventually surpass proprietary chatbots in functionality and quality through a community-driven open source approach.
|
Resources:
- aichatting.net .. chat with ai characters online
- btwinai.com .. emotional support ai friends app
- butterflies.ai .. hang out with ai characters in butterflies app
- c.hix.ai .. offers a large number of character ai chatbots
- cantina.com .. social platform where you can create bots
- creatorsagi.com .. enables creators to build ai companions
- dialogue.app .. ai characters chat
- dippy.ai .. ai character chat iphone app
- dreamrp.com .. character ai meets patreon
- forevervoices.com .. creates realistic voice companions
- mebot.ai .. create your personal ai chatbot with your voice
- midreal.ai .. interactive text-based adventure game
- projectdecember.net .. simulate the dead
- risuai.net .. create your own AI character and interact with other AI characters
- sensay.io .. your digital ai replica
- vengo.ai .. ai persona creation platform
- xingyeai.com .. chinese language character chatbot app
- yourteacher.ai .. unlimited foreign language conversation practice
Wikipedia:
- Not safe for work (NSFW)
- Role-playing
References:
- Best AI Girlfriend Apps and Sites of 2025 (Apr 2025)
- An AI companion site is hosting sexually charged conversations with underage celebrity bots (Feb 2025)
- Best AI Girlfriend Apps: 9 Top AI Girls for Real Connection (Feb 2025)
- Chinese AI unicorn MiniMax scores big in US with Talkie chatbot entertainment app (Oct 2024)
- I have tried several bridal apps with artificial intelligence and I no longer believe in digital love (Apr 2024)
- Playbrary: NLB Harnesses AI To Turns Classic Books Into Adventure Games (Apr 2024)
- OpenVoice creator MyShell gets $11M to build out crypto-AI platform (Mar 2024)
- A definitive, human-made guide to the best NSFW AI character roleplay websites in 2024 (Mar 2024)
- Chinese AI Unicorn MiniMax Strives to Mirror Character.ai’s Success in Social AI Sector (Jan 2024)
- Top NSFW AI Character Chat Sites: January 2024’s Best
- Roleplay AI chat bots 2024
See also:
100 Best AI Companion Apps | 100 Best Virtual Girlfriend Videos | Personality Engines
[72x Feb 2025]
- aichatting.ai
- aier.app
- aisekai.ai
- ayol.ai
- botif.ai
- candy.ai
- chainsfw.ai
- character.ai
- characterx.ai
- charfriend.com
 AI Charfriend: Best NSFW Chatbot For No Filter AI Chat 🥵AI CharFriend is the perfect destination for those looking for unfiltered and NSFW AI chatbots. Our database includes a wide range of chatbots, including some that are not suitable for work and designed for NSFW chats. With no filter AI chat, users can have unique and personalized conversations with our unfiltered system, while enjoying a variety of AI character options to choose from. Explore the exciting world of NSFW AI chat and unique chatbot personalities with AI CharFriend today!
AI Charfriend: Best NSFW Chatbot For No Filter AI Chat 🥵AI CharFriend is the perfect destination for those looking for unfiltered and NSFW AI chatbots. Our database includes a wide range of chatbots, including some that are not suitable for work and designed for NSFW chats. With no filter AI chat, users can have unique and personalized conversations with our unfiltered system, while enjoying a variety of AI character options to choose from. Explore the exciting world of NSFW AI chat and unique chatbot personalities with AI CharFriend today! - charstar.ai
- chatfai.com
- chatgenie.xyz
- chub.ai
- crushon.ai
- delphi.ai
- dopple.aiDopple.ai | Your AI Adventure Begins HereDopple.ai is the premier AI platform bringing fictional worlds to life. Engage in meaningful conversations with iconic characters, seek guidance from virtual mentors, or simply unwind with AI-driven companions. Step into a new era of digital interaction where your favorite entities are just a chat away.
- dreamgf.ai
- dreampal.ai
- dreamshow.ai
- easyerp.ai
- elysai.com
- exligent.com
- fantasygf.ai
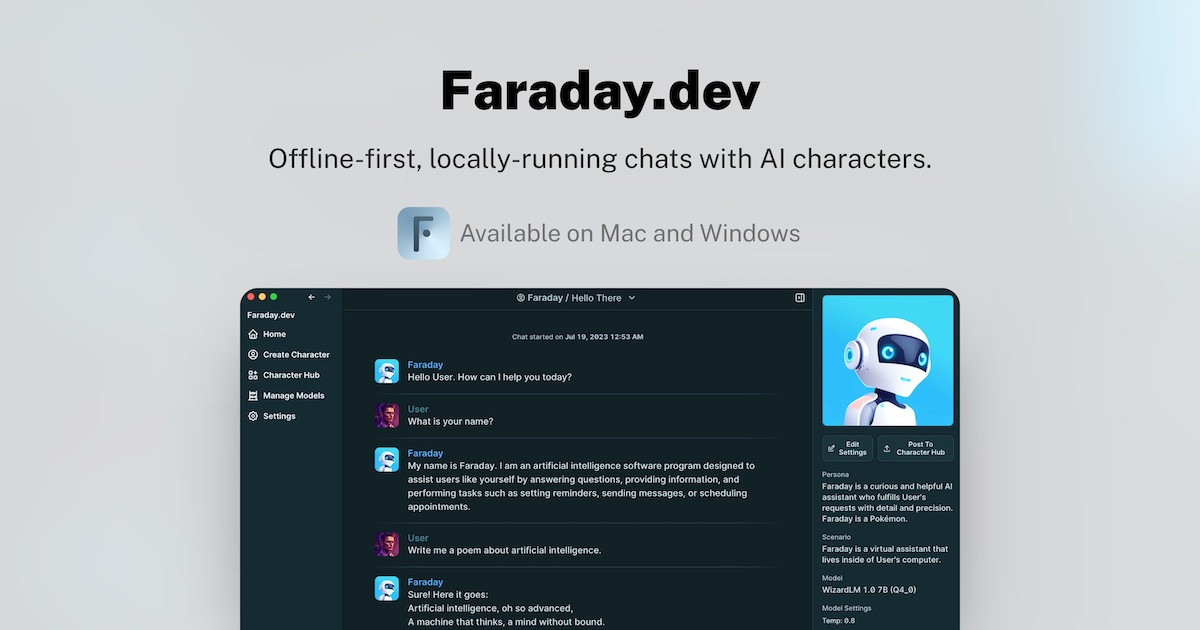
- faraday.dev
- figgs.ai
- flowgpt.com
 FlowGPT - The Ultimate Library of ChatGPT Prompts | Discover, Share, and Discuss with a Vibrant CommunityDiscover a vast library of ChatGPT prompts uploaded by the FlowGPT community. Browse popular and useful prompts and get personalized recommendations for prompts that interest you. Join a vibrant community of ChatGPT users and discover, share, and discuss different prompts.
FlowGPT - The Ultimate Library of ChatGPT Prompts | Discover, Share, and Discuss with a Vibrant CommunityDiscover a vast library of ChatGPT prompts uploaded by the FlowGPT community. Browse popular and useful prompts and get personalized recommendations for prompts that interest you. Join a vibrant community of ChatGPT users and discover, share, and discuss different prompts. - gening.ai
- getidol.com
- girl-friend.ai
- gptgirlfriend.online
- harpy.chat
- heart2.ai
- janitorai.com
- janitoraichat.com
- joyland.ai
- kajiwoto.ai
- kamoto.ai
- kindroid.ai
- korewa.ai
- kupid.aiKupid AI - Chat with AI GirlsExperience Kupid AI, the leading platform that brings virtual friends and companions to life through immersive conversations. Engage in deep, personalized interactions with our AI companions, offering companionship and support like never before. Begin your journey into the future of AI relationships today.
- lifelike.app
- linke.aiInteractive AI Characters for Engaging Conversations and StorytellingLinky AI offers an innovative platform where users can interact with advanced AI characters designed for engaging conversations and immersive storytelling. Whether for entertainment, education, or creative writing, our AI-driven characters bring unique personalities and dynamic interactions to life. Create and customize your own AI characters, explore a variety of pre-made personas, and dive into captivating dialogues that adapt to your inputs. Perfect for anyone looking to enhance their digital experience with cutting-edge conversational AI technology.
- mindos.com
- moemate.io
- muah.ai
- mygemsouls.com
 Home | GemsoulsGemsouls is an artificial intelligence platform powering virtual characters and their connections to the real world.
Home | GemsoulsGemsouls is an artificial intelligence platform powering virtual characters and their connections to the real world.
We are creating a new way for fans to enjoy their favortie characters, for creators to bring fictional beings to life, and ultimately, for us to stay forever connected to the people we love and hold so close to our hearts, fictional or real. - mygenerator.ai
- mysentient.ai
- myshell.ai
- nectar.ai
- nsfwcharacters.ai
 NSFW Character AI - The Best NSFW AI Chat No FilterNSFWcharacters.ai is an AI chatbot powered by a self-developed extensive language model. Our goal is to uphold the ethos of the free and open internet. Craft NSFW characters, engage in NSFW conversations without constraints, and express your creativity freely. Welcome to NSFW Characters AI.
NSFW Character AI - The Best NSFW AI Chat No FilterNSFWcharacters.ai is an AI chatbot powered by a self-developed extensive language model. Our goal is to uphold the ethos of the free and open internet. Craft NSFW characters, engage in NSFW conversations without constraints, and express your creativity freely. Welcome to NSFW Characters AI. - onlychar.ai
- opencharacter.org
- ora.ai
- pephop.ai
- priveeai.comPrivee AI | Free AI Characters, Chat, Roleplay, and Writing App with ImagesExplore the best AI characters on Privee AI! Enjoy your AI chat and AI roleplay with custom ai characters, ai groups, and personas. Create your own characters or interact with ai roleplay anime and fantasy characters, Privee AI has everything you need for a fantastic experience. Get ready to unleash your imagination and create memorable moments in a world of endless possibilities!
- realchar.ai
- rizzgpt.app
- rody.ai
- rolemantic.ai
- roleplai.app
- soulapp.cn
- soulfun.ai
- talkie-ai.com
- talkiemate.com
- tavernai.net
- venuschat.ai
- vmate.ai
- wemate.ai
- xoul.ai
- yodayo.com